* refactor: Unify examples interface with BaseRAGExample - Create BaseRAGExample base class for all RAG examples - Refactor 4 examples to use unified interface: - document_rag.py (replaces main_cli_example.py) - email_rag.py (replaces mail_reader_leann.py) - browser_rag.py (replaces google_history_reader_leann.py) - wechat_rag.py (replaces wechat_history_reader_leann.py) - Maintain 100% parameter compatibility with original files - Add interactive mode support for all examples - Unify parameter names (--max-items replaces --max-emails/--max-entries) - Update README.md with new examples usage - Add PARAMETER_CONSISTENCY.md documenting all parameter mappings - Keep main_cli_example.py for backward compatibility with migration notice All default values, LeannBuilder parameters, and chunking settings remain identical to ensure full compatibility with existing indexes. * fix: Update CI tests for new unified examples interface - Rename test_main_cli.py to test_document_rag.py - Update all references from main_cli_example.py to document_rag.py - Update tests/README.md documentation The tests now properly test the new unified interface while maintaining the same test coverage and functionality. * fix: Fix pre-commit issues and update tests - Fix import sorting and unused imports - Update type annotations to use built-in types (list, dict) instead of typing.List/Dict - Fix trailing whitespace and end-of-file issues - Fix Chinese fullwidth comma to regular comma - Update test_main_cli.py to test_document_rag.py - Add backward compatibility test for main_cli_example.py - Pass all pre-commit hooks (ruff, ruff-format, etc.) * refactor: Remove old example scripts and migration references - Delete old example scripts (mail_reader_leann.py, google_history_reader_leann.py, etc.) - Remove migration hints and backward compatibility - Update tests to use new unified examples directly - Clean up all references to old script names - Users now only see the new unified interface * fix: Restore embedding-mode parameter to all examples - All examples now have --embedding-mode parameter (unified interface benefit) - Default is 'sentence-transformers' (consistent with original behavior) - Users can now use OpenAI or MLX embeddings with any data source - Maintains functional equivalence with original scripts * docs: Improve parameter categorization in README - Clearly separate core (shared) vs specific parameters - Move LLM and embedding examples to 'Example Commands' section - Add descriptive comments for all specific parameters - Keep only truly data-source-specific parameters in specific sections * docs: Make example commands more representative - Add default values to parameter descriptions - Replace generic examples with real-world use cases - Focus on data-source-specific features in examples - Remove redundant demonstrations of common parameters * docs: Reorganize parameter documentation structure - Move common parameters to a dedicated section before all examples - Rename sections to 'X-Specific Arguments' for clarity - Remove duplicate common parameters from individual examples - Better information architecture for users * docs: polish applications * docs: Add CLI installation instructions - Add two installation options: venv and global uv tool - Clearly explain when to use each option - Make CLI more accessible for daily use * docs: Clarify CLI global installation process - Explain the transition from venv to global installation - Add upgrade command for global installation - Make it clear that global install allows usage without venv activation * docs: Add collapsible section for CLI installation - Wrap CLI installation instructions in details/summary tags - Keep consistent with other collapsible sections in README - Improve document readability and navigation * style: format * docs: Fix collapsible sections - Make Common Parameters collapsible (as it's lengthy reference material) - Keep CLI Installation visible (important for users to see immediately) - Better information hierarchy * docs: Add introduction for Common Parameters section - Add 'Flexible Configuration' heading with descriptive sentence - Create parallel structure with 'Generation Model Setup' section - Improve document flow and readability * docs: nit * fix: Fix issues in unified examples - Add smart path detection for data directory - Fix add_texts -> add_text method call - Handle both running from project root and examples directory * fix: Fix async/await and add_text issues in unified examples - Remove incorrect await from chat.ask() calls (not async) - Fix add_texts -> add_text method calls - Verify search-complexity correctly maps to efSearch parameter - All examples now run successfully * feat: Address review comments - Add complexity parameter to LeannChat initialization (default: search_complexity) - Fix chunk-size default in README documentation (256, not 2048) - Add more index building parameters as CLI arguments: - --backend-name (hnsw/diskann) - --graph-degree (default: 32) - --build-complexity (default: 64) - --no-compact (disable compact storage) - --no-recompute (disable embedding recomputation) - Update README to document all new parameters * feat: Add chunk-size parameters and improve file type filtering - Add --chunk-size and --chunk-overlap parameters to all RAG examples - Preserve original default values for each data source: - Document: 256/128 (optimized for general documents) - Email: 256/25 (smaller overlap for email threads) - Browser: 256/128 (standard for web content) - WeChat: 192/64 (smaller chunks for chat messages) - Make --file-types optional filter instead of restriction in document_rag - Update README to clarify interactive mode and parameter usage - Fix LLM default model documentation (gpt-4o, not gpt-4o-mini) * feat: Update documentation based on review feedback - Add MLX embedding example to README - Clarify examples/data content description (two papers, Pride and Prejudice, Chinese README) - Move chunk parameters to common parameters section - Remove duplicate chunk parameters from document-specific section * docs: Emphasize diverse data sources in examples/data description * fix: update default embedding models for better performance - Change WeChat, Browser, and Email RAG examples to use all-MiniLM-L6-v2 - Previous Qwen/Qwen3-Embedding-0.6B was too slow for these use cases - all-MiniLM-L6-v2 is a fast 384-dim model, ideal for large-scale personal data * add response highlight * change rebuild logic * fix some example * feat: check if k is larger than #docs * fix: WeChat history reader bugs and refactor wechat_rag to use unified architecture * fix email wrong -1 to process all file * refactor: reorgnize all examples/ and test/ * refactor: reorganize examples and add link checker * fix: add init.py * fix: handle certificate errors in link checker * fix wechat * merge * docs: update README to use proper module imports for apps - Change from 'python apps/xxx.py' to 'python -m apps.xxx' - More professional and pythonic module calling - Ensures proper module resolution and imports - Better separation between apps/ (production tools) and examples/ (demos) --------- Co-authored-by: yichuan520030910320 <yichuan_wang@berkeley.edu>
The smallest vector index in the world. RAG Everything with LEANN!
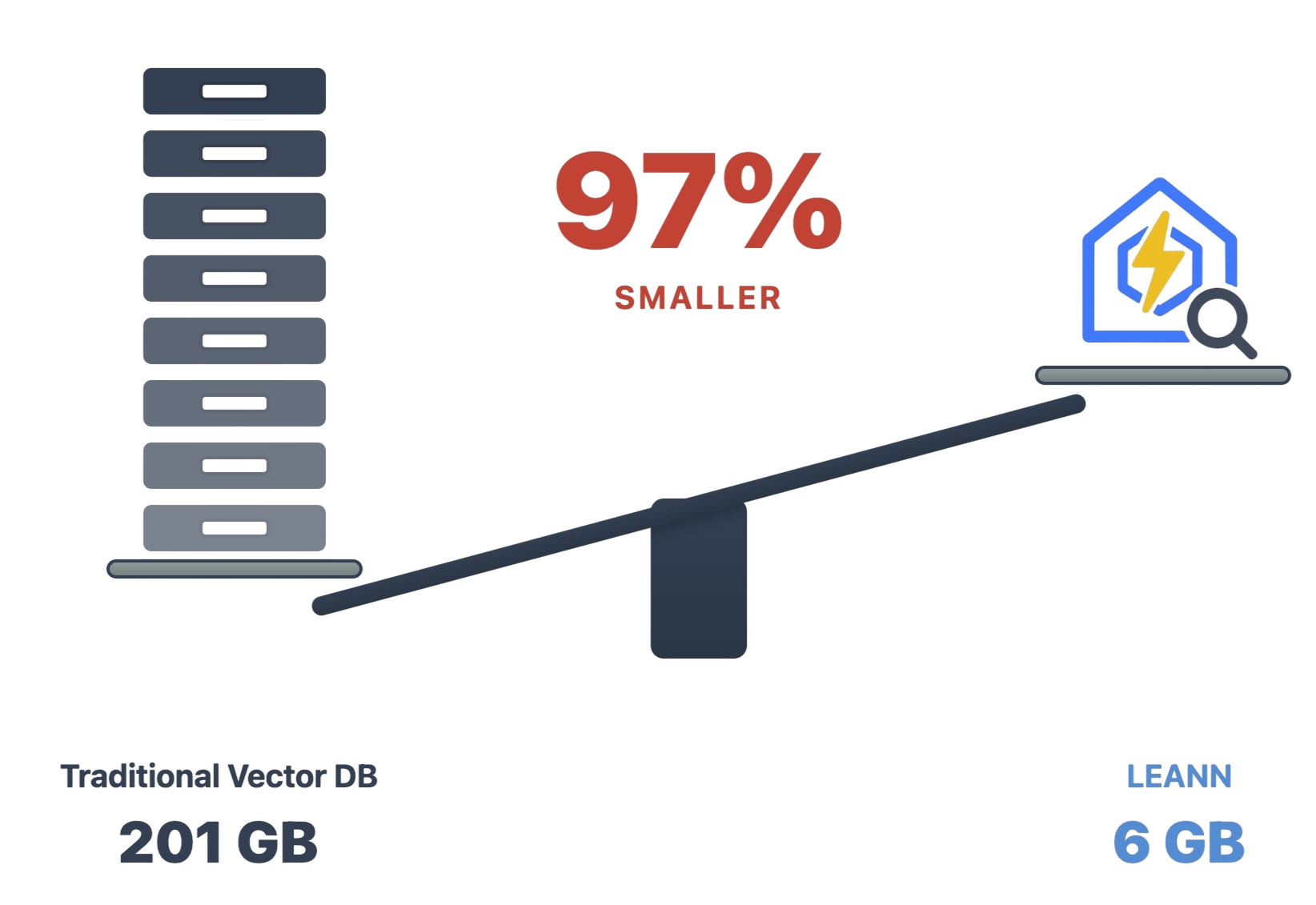
LEANN is an innovative vector database that democratizes personal AI. Transform your laptop into a powerful RAG system that can index and search through millions of documents while using 97% less storage than traditional solutions without accuracy loss.
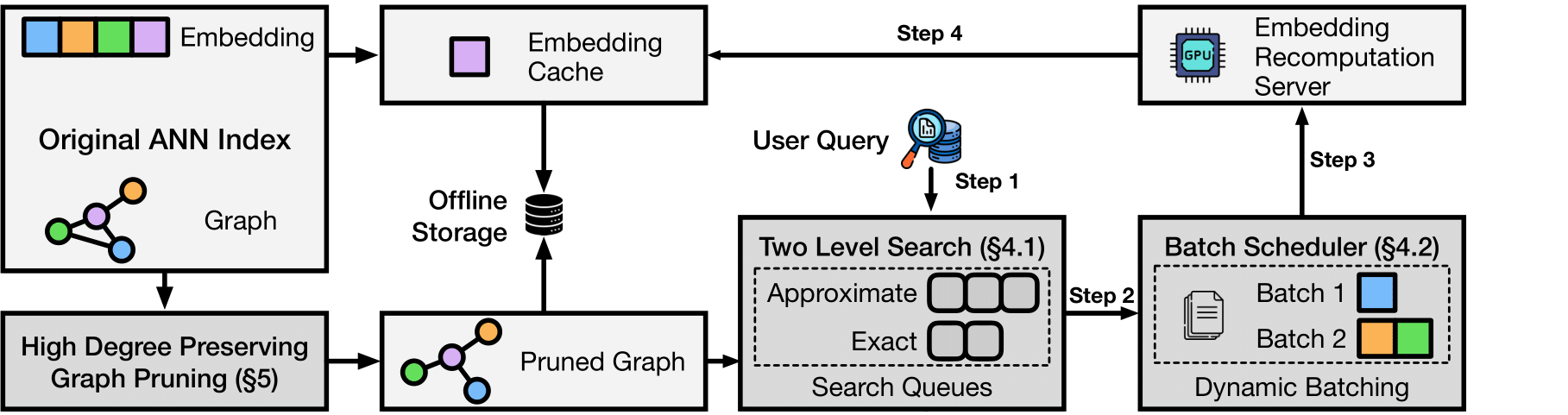
LEANN achieves this through graph-based selective recomputation with high-degree preserving pruning, computing embeddings on-demand instead of storing them all. Illustration Fig → | Paper →
Ready to RAG Everything? Transform your laptop into a personal AI assistant that can search your file system, emails, browser history, chat history, or external knowledge bases (i.e., 60M documents) - all on your laptop, with zero cloud costs and complete privacy.
Why LEANN?
The numbers speak for themselves: Index 60 million Wikipedia chunks in just 6GB instead of 201GB. From emails to browser history, everything fits on your laptop. See detailed benchmarks for different applications below ↓
🔒 Privacy: Your data never leaves your laptop. No OpenAI, no cloud, no "terms of service".
🪶 Lightweight: Graph-based recomputation eliminates heavy embedding storage, while smart graph pruning and CSR format minimize graph storage overhead. Always less storage, less memory usage!
📦 Portable: Transfer your entire knowledge base between devices (even with others) with minimal cost - your personal AI memory travels with you.
📈 Scalability: Handle messy personal data that would crash traditional vector DBs, easily managing your growing personalized data and agent generated memory!
✨ No Accuracy Loss: Maintain the same search quality as heavyweight solutions while using 97% less storage.
Installation
📦 Prerequisites: Install uv
Install uv first if you don't have it. Typically, you can install it with:
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
🚀 Quick Install
Clone the repository to access all examples and try amazing applications,
git clone https://github.com/yichuan-w/LEANN.git leann
cd leann
and install LEANN from PyPI to run them immediately:
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install leann
🔧 Build from Source (Recommended for development)
git clone https://github.com/yichuan-w/LEANN.git leann
cd leann
git submodule update --init --recursive
macOS:
brew install llvm libomp boost protobuf zeromq pkgconf
CC=$(brew --prefix llvm)/bin/clang CXX=$(brew --prefix llvm)/bin/clang++ uv sync
Linux:
sudo apt-get install libomp-dev libboost-all-dev protobuf-compiler libabsl-dev libmkl-full-dev libaio-dev libzmq3-dev
uv sync
Quick Start
Our declarative API makes RAG as easy as writing a config file.
Check out demo.ipynb or
from leann import LeannBuilder, LeannSearcher, LeannChat
from pathlib import Path
INDEX_PATH = str(Path("./").resolve() / "demo.leann")
# Build an index
builder = LeannBuilder(backend_name="hnsw")
builder.add_text("LEANN saves 97% storage compared to traditional vector databases.")
builder.add_text("Tung Tung Tung Sahur called—they need their banana‑crocodile hybrid back")
builder.build_index(INDEX_PATH)
# Search
searcher = LeannSearcher(INDEX_PATH)
results = searcher.search("fantastical AI-generated creatures", top_k=1)
# Chat with your data
chat = LeannChat(INDEX_PATH, llm_config={"type": "hf", "model": "Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B"})
response = chat.ask("How much storage does LEANN save?", top_k=1)
RAG on Everything!
LEANN supports RAG on various data sources including documents (.pdf, .txt, .md), Apple Mail, Google Search History, WeChat, and more.
Generation Model Setup
LEANN supports multiple LLM providers for text generation (OpenAI API, HuggingFace, Ollama).
🔑 OpenAI API Setup (Default)
Set your OpenAI API key as an environment variable:
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your-api-key-here"
🔧 Ollama Setup (Recommended for full privacy)
macOS:
First, download Ollama for macOS.
# Pull a lightweight model (recommended for consumer hardware)
ollama pull llama3.2:1b
Linux:
# Install Ollama
curl -fsSL https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
# Start Ollama service manually
ollama serve &
# Pull a lightweight model (recommended for consumer hardware)
ollama pull llama3.2:1b
Flexible Configuration
LEANN provides flexible parameters for embedding models, search strategies, and data processing to fit your specific needs.
📋 Click to expand: Common Parameters (Available in All Examples)
All RAG examples share these common parameters. Interactive mode is available in all examples - simply run without --query to start a continuous Q&A session where you can ask multiple questions. Type 'quit' to exit.
# Core Parameters (General preprocessing for all examples)
--index-dir DIR # Directory to store the index (default: current directory)
--query "YOUR QUESTION" # Single query mode. Omit for interactive chat (type 'quit' to exit), and now you can play with your index interactively
--max-items N # Limit data preprocessing (default: -1, process all data)
--force-rebuild # Force rebuild index even if it exists
# Embedding Parameters
--embedding-model MODEL # e.g., facebook/contriever, text-embedding-3-small or mlx-community/multilingual-e5-base-mlx
--embedding-mode MODE # sentence-transformers, openai, or mlx
# LLM Parameters (Text generation models)
--llm TYPE # LLM backend: openai, ollama, or hf (default: openai)
--llm-model MODEL # Model name (default: gpt-4o) e.g., gpt-4o-mini, llama3.2:1b, Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B-Instruct
# Search Parameters
--top-k N # Number of results to retrieve (default: 20)
--search-complexity N # Search complexity for graph traversal (default: 32)
# Chunking Parameters
--chunk-size N # Size of text chunks (default varies by source: 256 for most, 192 for WeChat)
--chunk-overlap N # Overlap between chunks (default varies: 25-128 depending on source)
# Index Building Parameters
--backend-name NAME # Backend to use: hnsw or diskann (default: hnsw)
--graph-degree N # Graph degree for index construction (default: 32)
--build-complexity N # Build complexity for index construction (default: 64)
--no-compact # Disable compact index storage (compact storage IS enabled to save storage by default)
--no-recompute # Disable embedding recomputation (recomputation IS enabled to save storage by default)
📄 Personal Data Manager: Process Any Documents (.pdf, .txt, .md)!
Ask questions directly about your personal PDFs, documents, and any directory containing your files!
The example below asks a question about summarizing our paper (uses default data in data/, which is a directory with diverse data sources: two papers, Pride and Prejudice, and a README in Chinese) and this is the easiest example to run here:
source .venv/bin/activate # Don't forget to activate the virtual environment
python -m apps.document_rag --query "What are the main techniques LEANN explores?"
📋 Click to expand: Document-Specific Arguments
Parameters
--data-dir DIR # Directory containing documents to process (default: data)
--file-types .ext .ext # Filter by specific file types (optional - all LlamaIndex supported types if omitted)
Example Commands
# Process all documents with larger chunks for academic papers
python -m apps.document_rag --data-dir "~/Documents/Papers" --chunk-size 1024
# Filter only markdown and Python files with smaller chunks
python -m apps.document_rag --data-dir "./docs" --chunk-size 256 --file-types .md .py
📧 Your Personal Email Secretary: RAG on Apple Mail!
Note: The examples below currently support macOS only. Windows support coming soon.
Before running the example below, you need to grant full disk access to your terminal/VS Code in System Preferences → Privacy & Security → Full Disk Access.
python -m apps.email_rag --query "What's the food I ordered by DoorDash or Uber Eats mostly?"
780K email chunks → 78MB storage. Finally, search your email like you search Google.
📋 Click to expand: Email-Specific Arguments
Parameters
--mail-path PATH # Path to specific mail directory (auto-detects if omitted)
--include-html # Include HTML content in processing (useful for newsletters)
Example Commands
# Search work emails from a specific account
python -m apps.email_rag --mail-path "~/Library/Mail/V10/WORK_ACCOUNT"
# Find all receipts and order confirmations (includes HTML)
python -m apps.email_rag --query "receipt order confirmation invoice" --include-html
📋 Click to expand: Example queries you can try
Once the index is built, you can ask questions like:
- "Find emails from my boss about deadlines"
- "What did John say about the project timeline?"
- "Show me emails about travel expenses"
🔍 Time Machine for the Web: RAG Your Entire Chrome Browser History!
python -m apps.browser_rag --query "Tell me my browser history about machine learning?"
38K browser entries → 6MB storage. Your browser history becomes your personal search engine.
📋 Click to expand: Browser-Specific Arguments
Parameters
--chrome-profile PATH # Path to Chrome profile directory (auto-detects if omitted)
Example Commands
# Search academic research from your browsing history
python -m apps.browser_rag --query "arxiv papers machine learning transformer architecture"
# Track competitor analysis across work profile
python -m apps.browser_rag --chrome-profile "~/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Work Profile" --max-items 5000
📋 Click to expand: How to find your Chrome profile
The default Chrome profile path is configured for a typical macOS setup. If you need to find your specific Chrome profile:
- Open Terminal
- Run:
ls ~/Library/Application\ Support/Google/Chrome/ - Look for folders like "Default", "Profile 1", "Profile 2", etc.
- Use the full path as your
--chrome-profileargument
Common Chrome profile locations:
- macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Google/Chrome/Default - Linux:
~/.config/google-chrome/Default
💬 Click to expand: Example queries you can try
Once the index is built, you can ask questions like:
- "What websites did I visit about machine learning?"
- "Find my search history about programming"
- "What YouTube videos did I watch recently?"
- "Show me websites I visited about travel planning"
💬 WeChat Detective: Unlock Your Golden Memories!
python -m apps.wechat_rag --query "Show me all group chats about weekend plans"
400K messages → 64MB storage Search years of chat history in any language.
🔧 Click to expand: Installation Requirements
First, you need to install the WeChat exporter,
brew install sunnyyoung/repo/wechattweak-cli
or install it manually (if you have issues with Homebrew):
sudo packages/wechat-exporter/wechattweak-cli install
Troubleshooting:
- Installation issues: Check the WeChatTweak-CLI issues page
- Export errors: If you encounter the error below, try restarting WeChat
Failed to export WeChat data. Please ensure WeChat is running and WeChatTweak is installed. Failed to find or export WeChat data. Exiting.
📋 Click to expand: WeChat-Specific Arguments
Parameters
--export-dir DIR # Directory to store exported WeChat data (default: wechat_export_direct)
--force-export # Force re-export even if data exists
Example Commands
# Search for travel plans discussed in group chats
python -m apps.wechat_rag --query "travel plans" --max-items 10000
# Re-export and search recent chats (useful after new messages)
python -m apps.wechat_rag --force-export --query "work schedule"
💬 Click to expand: Example queries you can try
Once the index is built, you can ask questions like:
- "我想买魔术师约翰逊的球衣,给我一些对应聊天记录?" (Chinese: Show me chat records about buying Magic Johnson's jersey)
🖥️ Command Line Interface
LEANN includes a powerful CLI for document processing and search. Perfect for quick document indexing and interactive chat.
Installation
If you followed the Quick Start, leann is already installed in your virtual environment:
source .venv/bin/activate
leann --help
To make it globally available (recommended for daily use):
# Install the LEANN CLI globally using uv tool
uv tool install leann
# Now you can use leann from anywhere without activating venv
leann --help
Usage Examples
# Build an index from documents
leann build my-docs --docs ./documents
# Search your documents
leann search my-docs "machine learning concepts"
# Interactive chat with your documents
leann ask my-docs --interactive
# List all your indexes
leann list
Key CLI features:
- Auto-detects document formats (PDF, TXT, MD, DOCX)
- Smart text chunking with overlap
- Multiple LLM providers (Ollama, OpenAI, HuggingFace)
- Organized index storage in
~/.leann/indexes/ - Support for advanced search parameters
📋 Click to expand: Complete CLI Reference
Build Command:
leann build INDEX_NAME --docs DIRECTORY [OPTIONS]
Options:
--backend {hnsw,diskann} Backend to use (default: hnsw)
--embedding-model MODEL Embedding model (default: facebook/contriever)
--graph-degree N Graph degree (default: 32)
--complexity N Build complexity (default: 64)
--force Force rebuild existing index
--compact Use compact storage (default: true)
--recompute Enable recomputation (default: true)
Search Command:
leann search INDEX_NAME QUERY [OPTIONS]
Options:
--top-k N Number of results (default: 5)
--complexity N Search complexity (default: 64)
--recompute-embeddings Use recomputation for highest accuracy
--pruning-strategy {global,local,proportional}
Ask Command:
leann ask INDEX_NAME [OPTIONS]
Options:
--llm {ollama,openai,hf} LLM provider (default: ollama)
--model MODEL Model name (default: qwen3:8b)
--interactive Interactive chat mode
--top-k N Retrieval count (default: 20)
🏗️ Architecture & How It Works
The magic: Most vector DBs store every single embedding (expensive). LEANN stores a pruned graph structure (cheap) and recomputes embeddings only when needed (fast).
Core techniques:
- Graph-based selective recomputation: Only compute embeddings for nodes in the search path
- High-degree preserving pruning: Keep important "hub" nodes while removing redundant connections
- Dynamic batching: Efficiently batch embedding computations for GPU utilization
- Two-level search: Smart graph traversal that prioritizes promising nodes
Backends: DiskANN or HNSW - pick what works for your data size.
Benchmarks
Simple Example: Compare LEANN vs FAISS →
📊 Storage Comparison
| System | DPR (2.1M) | Wiki (60M) | Chat (400K) | Email (780K) | Browser (38K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional vector database (e.g., FAISS) | 3.8 GB | 201 GB | 1.8 GB | 2.4 GB | 130 MB |
| LEANN | 324 MB | 6 GB | 64 MB | 79 MB | 6.4 MB |
| Savings | 91% | 97% | 97% | 97% | 95% |
Reproduce Our Results
uv pip install -e ".[dev]" # Install dev dependencies
python benchmarks/run_evaluation.py data/indices/dpr/dpr_diskann # DPR dataset
python benchmarks/run_evaluation.py data/indices/rpj_wiki/rpj_wiki.index # Wikipedia
The evaluation script downloads data automatically on first run. The last three results were tested with partial personal data, and you can reproduce them with your own data!
🔬 Paper
If you find Leann useful, please cite:
LEANN: A Low-Storage Vector Index
@misc{wang2025leannlowstoragevectorindex,
title={LEANN: A Low-Storage Vector Index},
author={Yichuan Wang and Shu Liu and Zhifei Li and Yongji Wu and Ziming Mao and Yilong Zhao and Xiao Yan and Zhiying Xu and Yang Zhou and Ion Stoica and Sewon Min and Matei Zaharia and Joseph E. Gonzalez},
year={2025},
eprint={2506.08276},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.DB},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08276},
}
✨ Detailed Features →
🤝 CONTRIBUTING →
❓ FAQ →
📈 Roadmap →
📄 License
MIT License - see LICENSE for details.
🙏 Acknowledgments
This work is done at Berkeley Sky Computing Lab.
⭐ Star us on GitHub if Leann is useful for your research or applications!
Made with ❤️ by the Leann team